

In the examples above, we used the shorthand overflow property. This includes the auto and hidden values. Note: Bootstrap CSS only supports two values for the overflow property, by default. In the example below, the first div has overflow and therefore a scrollbar and the second div does not. Meaning, the box has scrollable overflow.
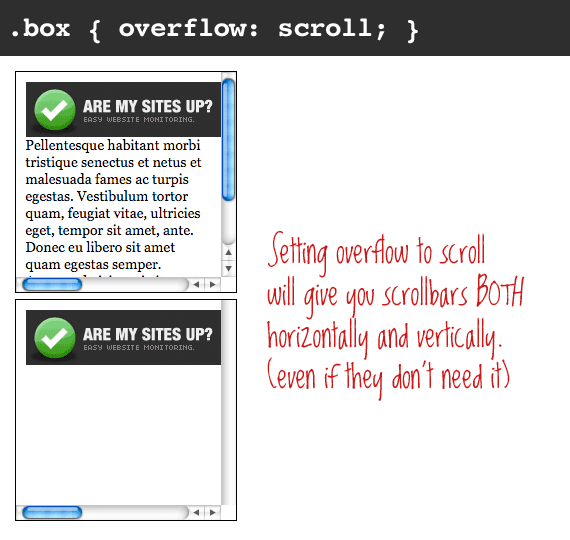
Overflow:auto means that the overflow will be clipped at the box's padding edge and a scroll bar will be added if necessary. Only one has scrollable overflow and a scrollbar, however. In the example below, both divs are defined with overflow:auto. The “auto” value is similar to scroll - but only adds a scrollbar when the box has overflow. In the example below, a scrollbar is added. Overflow:scroll means that the overflow will be clipped at the box's padding edge, but a scrolling mechanism will be added so that users will be able to scroll to see the content that isn't visible. However, a scrollbar or paneer will be added so that users can scroll to see the content that’s not visible. If you’d like to hide overflow from rendering outside the element’s box but enable users to view that content, you can set the overflow property to “scroll.” The overflow will still be clipped at the box’s padding edge. This value differs from "clip" in that it still allows programmatic scrolling, which means the box is technically a scroll container. Instead, it will be clipped at the box's padding edge. Overflow:hidden means that the overflow will not render outside the element’s box. A user could use the mechanisms defined by the CSSOM View Module, for example, to see the hidden content. However, this value still allows programmatic scrolling, which means the box is technically a scroll container. To hide overflow from rendering outside the element’s box, you can set the overflow property to “hidden.” This will clip the content at the box’s padding edge and not allow the user to view the content beyond that edge by scrolling or dragging their finger on a touch screen or any other means. Since the CSS overflow property is set to visible by default, you don't have to define it in your CSS. Overflow:visible means that the overflow will render outside the element’s box and potentially overlap with other elements on the page, as shown below. Meaning, you don’t need to set the CSS overflow property to “visible” unless you’re overriding CSS in an external stylesheet or somewhere else on your site. Instead, it will render outside the element’s box and potentially overlap with other elements on the page.īy default, the CSS overflow property is set to visible. Visible means that the overflow will not be clipped. To do so, you need to use the following property values. You can let the content render outside the element’s box, clip the content, or clip the content and add a scrollbar. The CSS overflow property provides a few options for controlling overflow. When the content of an HTML element extends beyond any of the box’s edges - whether that’s the content edge, padding edge, border edge, or margin edge - it is called overflow. This box is made up of four layers: the content itself, padding, a border, and a margin, as illustrated below. You can use the CSS overflow property to control what happens to the overflow.īefore we take a closer look at the overflow property, let’s clarify what we meant by the “element’s box.” According to the CSS box model, a rectangular box is generated for HTML elements. This occurs when a block element has a specified height that’s too small for the content it contains.

Furthermore, the content that is being displayed outside the box boundary will not disturb the alignment of other surrounding elements.In CSS, overflow refers to any content that is too big for an element’s box. Suppose if your content is placed inside a box and is overflowing then this value will display the content exceeding the box area. This is a default value of the overflow property. Like other CSS properties, the overflow property also exhibits certain values which are explained in depth below. The overflow property controls the behavior of the content that overflows the specified area of an element, moreover, the overflow property is designed for block-level elements only.

This post is designed to enlighten its readers about the details of the overflow property in CSS. You can choose what to do with the overflowing content using the CSS overflow property. While developing websites we often come across situations where the content present in certain HTML elements overflow.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
